Are there really any differences between stocks and bonds? What is the most advantageous investment, if any?
Those are the kinds of things that first-time investors contemplate on a regular basis. In order to better understand how these investment possibilities differ from one another, let’s take a closer look at each one individually.
When it comes to investment, stocks and bonds are frequently discussed in the same sentence.
However, there are significant differences between them in terms of risk, reward potential, and how you get them. That is why it is so critical to conduct thorough research before putting your hard-earned money at risk.
Table of Contents
What’s a Stock?
Stocks are “share of ownership in a company” from the standpoints of investment and financial planning.
Other words that are frequently used interchangeably with the word stock are the terms “share” and “equity,” among others.
Regardless of the terminology used, holding stock indicates that you own a portion of a company, and the value of your shares increases as the company rises in importance. Actually, it isn’t quite the case, at least not technically speaking.
Where Do Stocks Come From?
You are not a shareholder in the corporation itself. Instead, you become the owner of one unit’s worth of that company’s assets (earnings).
So why would a corporation want to sell you shares in the first place?
The reasons why a company decides to raise cash by selling shares of ownership in their company will differ from one another.
However, in general, corporations utilize stock sales as a means of raising operating money to fund their operations.
How To Find Stocks to Invest In?
It will be your responsibility to conduct due diligence before making a decision on which stocks to acquire in order to ensure that you are comfortable contributing financing to a certain business.
But, once you’ve decided which stocks to invest in, where do you go to actually purchase them?
To be sure, you can’t just walk up to Company A, knock on their door, and ask to purchase a single unit of their stock.
US Stock Exchanges
So, where can you get your hands on some stock?
The NYSE (New York Stock Exchange), the NASDAQ (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations), and the AMEX (American Stock Exchange) are examples of public stock exchanges.
You may already be acquainted with (American Stock Exchange).
Overall, there are a total of 13 such stock exchanges in the United States.
Top 10 NASDAQ Stocks
One of the biggest sectors of the US economy is the tech industry.
The company that comprise the main Exchange Traded Fund (ETF) for this sector have been driving the overall market over the last 10 years at least.
As of this writing, here is the table with these leading companies.
Each with their respective weighting into the NASDAQ index.
| No. | Company | Symbol | Weight | Price | Chg |
| 1 | Apple Inc. | AAPL | 11.3% | 150.09 | -0.31% |
| 2 | Microsoft Corp. | MSFT | 10.4% | 303.23 | 0.61 |
| 3 | Amazon.com Inc. | AMZN | 7.4% | 3,310.00 | 4.22 |
| 4 | Alphabet Inc. | GOOG | 4.1% | 2,853.96 | 5.99 |
| 5 | Facebook Inc. | FB | 3.9% | 365.84 | 0.33 |
| 6 | Alphabet Inc. | GOOGL | 3.8% | 2,829.35 | 4.12 |
| 7 | Tesla Inc. | TSLA | 3.8% | 707.32 | -1.17 |
| 8 | NVIDIA Corp. | NVDA | 3.7% | 217.37 | -0.56 |
| 9 | Paypal Holdings Inc. | PYPL | 2.2% | 279.93 | 0.42 |
| 10 | Adobe Inc. | ADBE | 2.1% | 659.84 | 2.60 |
Analysis of Top 10 NASDAQ Stocks Over 10 Years
The gain and amount presented in the table below for each stock are based on the $1000 if you invested them 10 years ago.
| No. | Stock | Symbol | Amount in $ | % Gain |
| 1 | Apple Inc. | AAPL | $11,628.19 | 1,062.82% |
| 2 | Microsoft Corp. | MSFT | $12,153.41 | 1,115.34% |
| 3 | Amazon.com Inc. | AMZN | $17,957.70 | 1,695.77% |
| 4 | Alphabet Inc. | GOOG | $9,024.40 | 802.44% |
| 5 | Facebook Inc. | FB | $11,122.21 | 1012.22% |
| 6 | Alphabet Inc. | GOOGL | $11,055.16 | 1,005.52% |
| 7 | Tesla Inc. | TSLA | $130,466.91 | 12,946.69% |
| 8 | NVIDIA Corp. | NVDA | $52,835.99 | 5,183.60% |
| 9 | Paypal Holdings Inc. | PYPL | $6,481.10 | 668.73% |
| 10 | Adobe Inc. | ADBE | $20,120.05 | 1,912.01% |
Some of the growth percentages are just flat out unbelievable.
Paypal (Ticker:PYPL) has the worst gain over the last 10 years on this list.
Yet that growth is almost 700% !!
Do you know many investment can turn your money 7 folds in 10 years ?
Google’s parent company Alphabet has the second worst return from the list over the last decade and that is 800%.
All the remaining have grown 10-fold at least over the last 10 years thus making this an exceptional era for stock growth.
Therefore, these returns alone are sufficient to understand why more and more investors who have time (meaning not near their retirement age) are drawn to the stock market rather than bonds.
Why Should You Choose NASDAQ?
The Nasdaq is the world’s second-largest stock exchange.
The Nasdaq is home to over 3,700 public firms with a combined market capitalization of more than $19 trillion—only slightly less than the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), which has a total listed market capitalization of $25.5 trillion.
The Evolution of the NASDAQ
Nasdaq established itself as the first all-electronic exchange, and it continues to be the preferred platform for many top technology businesses.
The NASDAQ-100 Index is significant because it has a significant impact on both the local and global economies.
It advises society and investors on the best non-financial companies. For businesses, it is a well-known and reputable exchange on which to list their shares.
If they include in the index, it might have a significant impact on their financial performance.
Additionally, the index is suitable for incorporating companies that are at the cutting edge of innovation across all industries covered.
More broadly, the Nasdaq provides a plethora of stock options.
How Fractional Shares Will Help You With Hight Stock Prices?
More often, big-name stocks come with hefty price tags. As of August 2020, one share of Alphabet, Inc., the parent company of Google, valued at more than $1,500.
While one share of Amazon.com, Inc. valued at more than $3,000.
Fractional shares, on the other hand, allow you to purchase even the most expensive stocks and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) for as little as one dollar.
Purchasing a fractional stock is advantageous for novice investors who may not have large balances available to purchase certain stocks or ETFs.
Additionally, they let you quickly diversify a smaller portfolio by investing in companies that would be out of reach otherwise.
The Advantages of Fractional Shares
Begin investing with small funds
If you’re just getting started and don’t have a sizable investment portfolio, fractional shares can make a significant impact.
They enable you to enter the market instantly and begin reaping the benefits of compounding profits.
Diversify your portfolio on a shoestring budget
Diversification is a fundamental principle of portfolio development. By diversifying your holdings of equities and, more specifically, ETFs, you may minimize the risk of losing money if a single asset falls.
Because fractional investing enables you to purchase several shares for between $1 and $5. You may be able to purchase a larger range of companies than you might otherwise.
Options for improved dollar cost averaging
Dollar-cost averaging is a strategy in which you invest a certain amount of money on a consistent basis.
This may allow you to pay less per share over time than you would if you purchased all of your shares at once.
Because dollar cost averaging is based on a stable dollar amount rather than a steady share portion, it works best when you can invest the entire amount.
Otherwise, a portion of your funds will have to stay in a cash account. Until you have sufficient funds to purchase a complete share.
Dividend Stocks and How Do They Work?
A stock dividend is a dividend payment in shares rather than cash to shareholders.
Although a stock dividend offers the advantage of paying shareholders without depleting the company’s cash reserves.
It does have the disadvantage of diluting earnings per share.
Generally, these stock distributions are issued as fractions of existing shares.
For instance, a company may declare a 5% stock dividend. Requiring it to issue 0.05 shares for each share held by existing shareholders.
Meaning that an owner of 100 shares would get five more shares.
Exactly how does a stock dividend work?
A stock dividend also referred to as a “scrip dividend,” is a payment of stock to existing owners in place of a cash dividend.
A company declares such dividends when it wants to reward its shareholders but lacks the necessary funds or wishes to conserve cash for other expenditures.
Dividends on stocks provide an investor with a tax advantage.
As with any stock, the dividend is tax-free until the investor sells it unless the company gives the choice of receiving the dividend in cash or shares.
A stock dividend may impose a restriction on the sale of newly acquired shares for a specified length of time.
This holding period generally begins the day after you buy a dividend stock. It is critical to understand the holding time for calculating eligible dividend tax treatment.
Top 5 Websites for Stocks Market Research
Finviz.com
Finviz is one of the greatest stock screeners for traders and investors accessible for free, as well as in a paid edition called Finviz Elite. Finviz is available in both a free and paid version.
It is a privately held firm that was established in June 2007 by Juraj Duris. Finviz is an abbreviation for “financial visualizations,” and its website receives around 18.75 million visits each month.
Tradingview
TradingView is a cloud-based charting and social networking program designed for active investment traders at all levels, from beginners to experts.
With a free account, you may access the most basic graphing, research, and analytical information accessible. Despite this, the majority of transactions must be executed outside of the platform due to the fact that only a limited number of brokerages are currently linked to TradingView.
Simply Wall Street
Al Bentley, the founder of Simply Wall St, established the company in Sydney, Australia, in 2014.
In order to assist investors in making stock selections for their portfolios based on fundamental research, Simply Wall St has created an online resource called Simply Wall St.
Webull
Webull, which was founded in 2017, is a relative newcomer to the brokerage industry, but it looks to have taken advantage of its late arrival to achieve success.
In other aspects, the company appears to have drawn ideas from current forerunners such as Robinhood, which cater to new and casual investors who want a fantastic mobile experience as well as a clean, simple desktop interface to get started with investing.
Webull, on the other hand, is an excellent alternative for more experienced active traders, as it provides in-depth charting, hundreds of technical indicators, advanced orders, Level II market data from Nasdaq, customization, and other features.
All of this is contained within an easily navigable and aesthetically pleasing platform.
E*Trade
Throughout the previous decade, ETRADE, a pioneer in online brokerage, has been hampered by charges that are higher than usual.
Equity and per-leg options charges were reduced to zero in October 2019, when ETRADE joined a majority of brokers in reducing commissions to $0.
There are three computer-based platforms and two fully-featured mobile apps available from E*TRADE, which will appeal to investors with a variety of investment styles and interests.
The company’s primary online platform, etrade.com, has been redesigned to make it easier to maneuver.
What Type of Investors Are Stocks For?
Anyone can purchase stocks on the stock exchange.
Each individual has his or her own motives for purchasing a stock, and each individual has a distinct trading personality.
Your trading personality is determined by how much risk you are prepared to take, what type of research you are willing to undertake, where you believe the economy is heading, and how much time you have on your hands to complete your trades.
Contrary to all of this uniqueness, trading styles may be broken down into a few basic categories. Take into consideration which method sounds the most like you.
Active-Investors
Active investors maintain track of the performance of their stocks, do extensive research, and keep up with the latest financial news on a regular basis.
Traders do not necessarily purchase one day and sell the next, but they do pay attention to changes in patterns and buy or sell in accordance with those changes in trends.
Despite the fact that this individual is an ardent investor who takes great care in making each investment decision, he or she does not necessarily keep an investment for the long term.
Passive investors
This type of investor does not always aim for the highest potential return on his or her investment.
Instead, the passive investor accepts fair returns in exchange for a reduced level of stress and more free time on his or her hands.
This individual may choose to invest in mutual funds in order to allow the funds’ money managers to make a purchase and sell choices.
He may choose to purchase individual shares of stock in well-established firms and hang onto that investment for a year or more.
Passive investors have a tendency to reduce the amount of stress they experience while making investing decisions by establishing parameters for adding new stocks to their portfolios.
For example, if their stocks grow by 20%, they may decide to sell part of them to realize the gains.
Speculator
Some investors are looking for opportunities to make money quickly. Then scour the market for stocks that are set to rise as a result of a pending transaction, and they buy them.
In order to make money, they scan the news for announcements about mergers that may benefit a business. And then they buy shares in those companies.
After a stock has made them some money, they tend to sell it.
Because they believe that they can repeat the practice of purchasing and selling on a regular basis. So beat the market.
Retirement Investors
When it comes to investing for retirement, people tend to modify their strategies as they get closer to retirement age.
When they are younger, they may choose a more confrontational response to conflict. This entails purchasing more risky stocks that have the potential to rise in value.
After midlife, such an investor may decide to switch to more moderate-risk stocks.
And then during retirement, they may decide to switch to dividend stocks that provide income.
Different Types of Stock
Not all stocks are equal by the executives of their respective companies, and they might be extremely different from one another in terms of performance.
Let’s have a look at what the stock markets have to offer and which kind of stocks are the most suitable for you.
Preferred Stock
The term “preferred” stock is a bit of a misnomer in this context.
At first glance, the preferred stock appears to be a greater type of stock than its counterpart, “common” stock. However, this is not the case.
This, on the other hand, is not correct.
To simply state that preferred stock differs from ordinary stock would be far more truthful.
Common Stock
Common stock is considerably more common than preferred stock in terms of being, well, common.
When a company decides to issue both preferred stock and common stock, the common stock issues in higher quantities than the preferred stock.
Occasionally, a company may choose not to issue any preferred stock at all.
Stocks and Diversification in Investment Portfolio
In order to create diversification in your investment portfolio, you must weigh the risks and rewards of different investments against one another.
Although this appears to be a simple concept in principle, putting it into practice is considerably more difficult.
By mixing asset types that are both riskier and less risky into a single investment portfolio, you can protect against losses while simultaneously keeping the door open to higher returns.
Preferential stock and ordinary stock are two primary forms of stock.
And you have just learned about the possible advantages and limits of each of them. As a result, you now understand that some types of stocks are riskier than others.
Another interesting and little-known fact regarding the preferred stock is that some financial professionals refer to preferred stock as the “bonds of the stock market.”
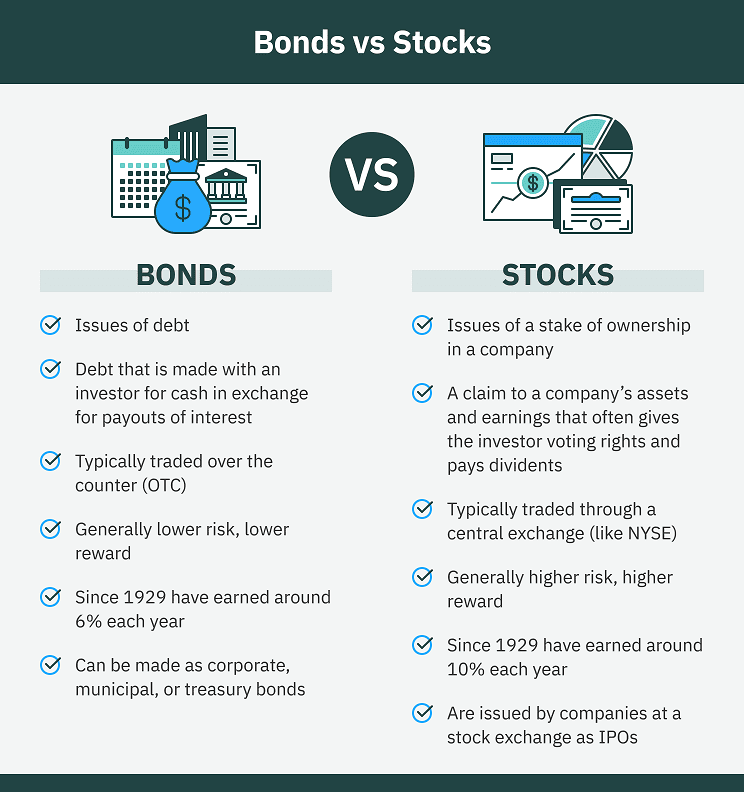
What’s a Bond?
Similar to how a stock represents a share of ownership in a company’s assets (income). A bond represents an IOU or a written promise to provide debt financing.
While bonds have lesser risk than stocks, this is not necessarily the case.
Company issues bonds to seek to raise cash from investors. Knowing the issuer—as well as the company’s history—is critical to understanding how to purchase bonds.
Understanding How Bonds Work
The company issuing the bonds has the ability to and does have an influence on the risk level associated with a particular bond.
Consider the following example: a bond issued by a government body is typically less hazardous than a bond issued by a private business by its nature.
Remember how we stated earlier that some financial experts consider preferred stocks to be the “bonds of the stock market?” Well, that is still true.
This is due to the fact that both assets provide a sort of fixed rate of return on investment.
Fixed dividends are paid on preferred stocks, while fixed interest is paid on bonds. However, the value of preferred stocks and bonds might vary in response to changes in the stock market.
Bonds, in principle, provide a guaranteed return even at the moment of issue of the bond.
It is possible to argue that bonds are less risky than preferred stock because, in the event of a company’s bankruptcy, bondholders will be first in line for reimbursement before preferred stockholders.
What Type of Investors Are Bonds For?
The following are some of the most common types of Investors who buy bonds:
Who Seeks for Income
The major rationale for purchasing a bond as an investment is for the income it provides.
The majority of bonds have a fixed interest rate, which means that investors will get regular semi-annual payments.
This provides certainty in terms of both cash flow and returns. It is something that other investments, such as stocks, can not provide.
For example, if you purchase a $1,000 bond that pays 5% interest, you will get $25 twice every year for the duration of your ownership of the bond.
At the conclusion of the bond’s life, which is the maturity date, you will also receive your $1,000 back.
Who Plays On Safe Side
There are dangers with all investments, but bonds are typically less hazardous than stocks. Few investments, stocks included, guarantee that your money will be returned to you. Specifically, at the end of the term like bonds do.
This repayment pledge, on the other hand, is only as good as the financial soundness of the issuer. Many bonds have letter grades by independent rating agencies to assist you in determining their relative security.
The bonds with the highest likelihood of making their payments on time award an AAA rating on most measures.
Who Seeks Diversification
Diversification is the process of investing in a variety of various types of assets. In order to reduce the overall risk of a portfolio.
Bonds play a significant part in most asset allocation models. Which split assets among stocks, money market funds, and other forms of investments, as well as in the stock market.
Because bonds tend to vary in value less than stocks.
They can help to smooth out the fluctuations in your portfolio. And lower your total risk by spreading out the risk.
For the most part, asset allocation models recommend that older or more cautious investors should maintain a greater percentage of their assets in money market funds or short-term bonds rather than inequities.
Common Types of Bonds
There are several sorts of connections, and it is vital to understand the differences between them.
Some bond types have a lower inherent risk than others, whilst others have a higher risk. There are four basic categories of bonds that we shall discuss, in addition to a few unique forms of bonds.
Government Bonds
Treasury bills, which are government bonds issued by the federal government, are a term that is often used incorrectly.
The term “note” refers to federal government bonds that will mature (fall due) in less than 10 years. And the federal government issues them.
Municipal Bonds
Municipal bonds issued by state or municipal governments to raise money.
The return on these bonds may be higher than that of other types of bonds.
But only if the region in which you invest is growing and developing. Municipalities that are in decline are less likely to repay your investment.
Interest Rates on Municipal Bonds
Some municipal bonds come with great tax advantages for higher income tax payers.
As such, those municipal bonds interest rate may not tell you the whole story after the return on investment.
Here is our research on some of the best Tax-exempt municipal bonds as of this writing.
| NAME | Ticker |
| Fidelity Tax Free Bond | FTABX |
| Vanguard High Yield | VWALX |
| Vanguard Intermediate Term | VWITX |
| Vanguard Long Term | VWULX |
| Vanguard Limited Term | VMLUX |
| Vanguard Short Term | VWSUX |
Agency Bonds
When bonds are issued by federal government agencies, these bonds are referred to as agency bonds. Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac bonds, for example, are examples of government-sponsored enterprises.
Corporate Bonds
Companies and companies may choose to issue corporate bonds in order to obtain cash for a number of different reasons.
These are frequently riskier than U.S. Treasury bonds, but they may also give greater rates of return.
Bonds and Diversification in Investment Portfolio
As you can see, bonds, like stocks, have various degrees of risk associated with them.
The degree of risk is determined by the issuing organization as well as the bond’s terms and conditions.
This means that just adding stocks and bonds to your investment portfolio will not be enough in terms of increasing your returns.
Portfolio Diversification
Creating a properly diversified portfolio also entails picking the appropriate categories. Moreover, the types of stocks and bonds in order to achieve a healthy balance between risk and return.
An investment bond’s rating can vary from AAA to D. The danger increases according to the lower the letter.
So-called “junk” bonds usually have the lowest ratings, which are based on the credit rating of the issuing corporation.
Or the length of time the company has been in business.
Differences Between Stocks and Bonds – Final Verdict
Stocks and bonds both have a place in the investment portfolios of experienced investors who are attempting to construct a properly diversified portfolio.
Stocks, as you are now aware, are fractional ownership interests in the assets or net worth of the issuing company.
Bonds, on the other hand, are debt instruments in their own right. With the possibility for interest income to use to reimburse the lender for the amount borrowed.
Preferential equities have a reduced risk of loss and a lower return on investment than ordinary stocks.
Government-issued bonds have a lower level of risk and. Therefore, a potentially lower rate of return than corporate bonds and callable bonds, respectively.
Investment in funds such as ETFs (exchange-traded funds) or mutual funds is one of the most straightforward methods.
In order to construct a portfolio that contains both greater and lower risk equities. As well as higher and lower risk bonds, among other things.
These funds may consist of a mixture of stocks and bonds. Or they may entirely consist of stocks or entirely comprised of bonds.

Hold a Master Degree in Electrical engineering from Texas A&M University.
African born – French Raised and US matured who speak 5 languages.
Active Stock Options Trader and Coach since 2014.
Most Swing Trade weekly Options and Specialize in 10-Baggers !
YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/c/SuccessfulTradings
Other Website: https://237answersblog.com/