I began trading in 2015 and started coaching in 2019. Book value trading represents one of the most reliable strategies for long-term wealth building. However, many investors misunderstand this fundamental approach completely. Therefore, this guide helps you master book value analysis for consistent market outperformance.
👉 In this guide, you will learn:
- 📊 How to identify undervalued stocks trading below book value
- 💰 Why book value matters more than popular metrics
- 🔍 Advanced screening techniques for book value opportunities
- 📈 When to buy, hold, and sell book value stocks
- ⚖️ Risk management strategies that protect your capital
- 💡 Common book value trading mistakes that cost money
- 🎯 Portfolio construction using book value principles
Book value provides a concrete foundation for investment decisions. Unfortunately, growth stock hype often overshadows this time-tested approach. Additionally, understanding book value separates serious investors from speculators completely.
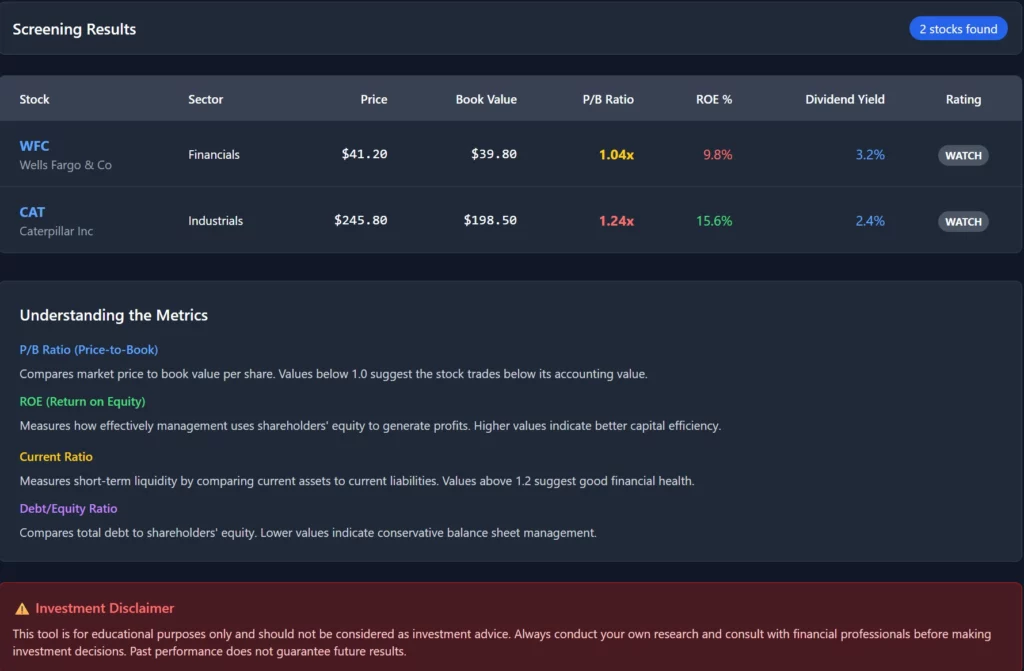
Table of Contents
Understanding Book Value Fundamentals 📚
Book value represents the accounting value of shareholder equity after subtracting liabilities from assets. Furthermore, it provides a baseline for determining whether stocks trade at reasonable prices. Additionally, companies trading below book value often present compelling investment opportunities.
What Book Value Actually Measures
Assets Minus Liabilities Equals Book Value Book value calculation involves straightforward accounting principles. Moreover, it reflects the theoretical liquidation value of shareholders’ stake. However, market prices frequently diverge from book value significantly.
Basic book value components:
- 🏢 Total assets including cash, inventory, equipment, and property
- 💸 Total liabilities including debt, accounts payable, and obligations
- 📊 Shareholders’ equity representing the residual ownership value
- 📈 Book value per share calculated by dividing equity by shares outstanding
Price-to-Book Ratio Analysis The price-to-book ratio compares market price to book value per share. Therefore, ratios below 1.0 indicate stocks trading below accounting value. Furthermore, this metric helps identify potentially undervalued opportunities systematically.
Price-to-book interpretation guidelines:
- 📉 P/B below 1.0: Stock trades below book value (potentially undervalued)
- 📊 P/B 1.0-2.0: Reasonable valuation for most industries
- 📈 P/B above 3.0: Premium valuation requiring strong growth justification
- 🔍 Compare P/B ratios within similar industry peer groups
Industries Where Book Value Matters Most
Financial Services and Banks Banks and financial institutions typically trade close to book value. Moreover, their assets consist primarily of cash and loans with clear valuations. Additionally, regulatory requirements ensure accurate asset reporting standards.
Why book value works for financials:
- 🏦 Assets primarily consist of cash and marketable securities
- 📊 Regulatory oversight ensures conservative accounting practices
- 💰 Business models depend on efficiently deploying shareholder capital
- 📈 Return on equity directly correlates with book value growth
Utilities and Infrastructure Companies Utility companies own substantial physical assets with clear valuations. Furthermore, regulated returns often correlate with book value investments. Additionally, stable cash flows support dividend payments consistently.
Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) REITs own tangible real estate assets with appraisable values. However, book value may lag current market prices. Therefore, adjusted book value calculations prove more accurate.
Manufacturing and Industrial Companies Companies with significant fixed assets often trade near book value. Moreover, asset-heavy businesses require substantial capital investments. Additionally, replacement costs provide valuation floors during downturns.
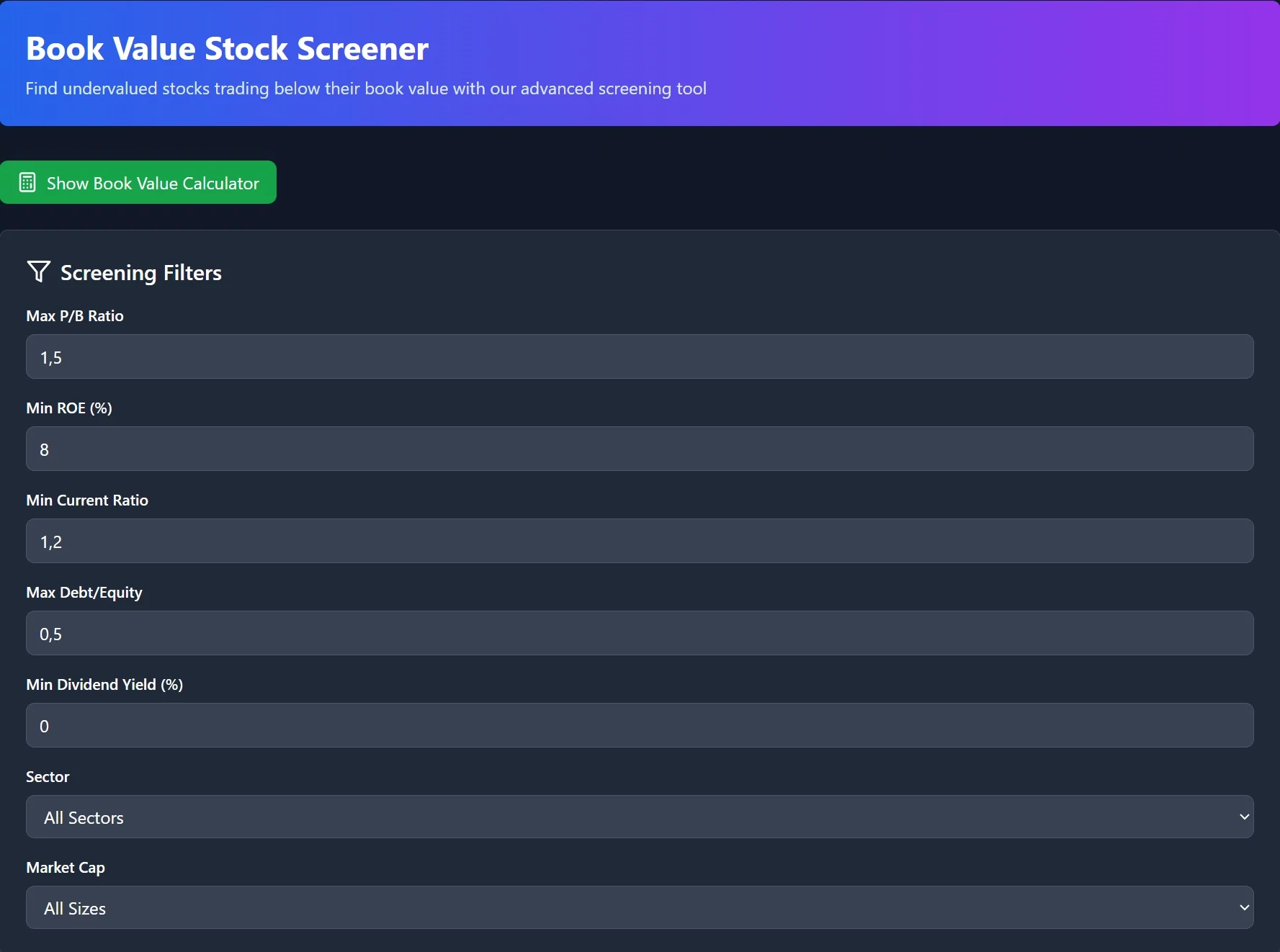
Advanced Book Value Screening Strategies 🔍
Successful book value investing requires systematic screening approaches. Furthermore, combining multiple criteria improves selection accuracy significantly. Therefore, developing robust screening processes becomes essential for consistent results.
Primary Screening Criteria
Price-to-Book Ratio Filters Start screening with P/B ratios below specific thresholds. However, avoid companies with artificially low ratios due to accounting issues. Moreover, verify that low ratios result from market conditions rather than fundamental problems.
Effective P/B screening parameters:
- 🎯 Primary screen: P/B ratio between 0.3 and 1.2
- 🎯 Industry comparison: P/B below sector median
- 🎯 Historical analysis: Current P/B below 5-year average
- 🎯 Trend evaluation: Stable or improving book value growth
Financial Health Indicators Book value analysis requires financially stable companies. Therefore, examine debt levels, cash flow, and profitability metrics. Additionally, avoid companies with deteriorating balance sheets despite low valuations.
Essential financial health metrics:
- 💰 Debt-to-equity ratio below 0.5 for non-financial companies
- 💰 Current ratio above 1.2 indicating adequate liquidity
- 💰 Positive operating cash flow over trailing twelve months
- 💰 Interest coverage ratio above 3.0 times earnings
Secondary Screening Filters
Return on Equity Consistency Companies earning consistent returns on book value create sustainable value. Furthermore, ROE trends indicate management effectiveness in capital deployment. However, avoid companies with consistently negative returns despite low valuations.
ROE evaluation criteria:
- 📈 Average ROE above 10% over past five years
- 📈 Consistent positive ROE without major negative years
- 📈 ROE improvement trend over recent periods
- 📈 ROE competitive within industry peer group
Dividend Coverage and Sustainability
Dividend-paying book value stocks provide income while waiting for appreciation. Moreover, sustainable dividends indicate financial strength and management confidence. Additionally, dividend cuts often signal deeper operational problems.
Dividend analysis factors:
- 💵 Payout ratio below 60% of earnings for sustainability
- 💵 Dividend coverage ratio above 1.5 times free cash flow
- 💵 No dividend cuts during past economic downturns
- 💵 Management commitment to maintaining dividend payments
Timing Your Book Value Trades ⏰
Market timing affects book value trading success significantly. However, patience proves more important than perfect entry points. Furthermore, systematic approaches outperform emotional decision-making consistently.
Optimal Entry Strategies
Market Cycle Considerations Book value opportunities increase during market downturns. Moreover, fear-driven selling creates pricing inefficiencies. Additionally, economic uncertainty often pushes solid companies below book value temporarily.
Best market conditions for book value investing:
- 📉 Bear markets when quality stocks trade at discounts
- 📉 Sector rotations away from value-oriented industries
- 📉 Economic uncertainty creating broad market pessimism
- 📉 Interest rate increases affecting growth stock valuations
Catalyst Identification Look for specific catalysts that could unlock book value. Furthermore, management changes, asset sales, or operational improvements drive appreciation. Additionally, activist investor involvement often catalyzes value realization.
Common book value catalysts:
- 🚀 Management turnover bringing operational improvements
- 🚀 Asset sales or spin-offs revealing hidden value
- 🚀 Share buyback programs reducing share count
- 🚀 Dividend increases signaling management confidence
Position Sizing and Portfolio Construction
Diversification Across Sectors Avoid concentrating book value investments in single industries. Instead, diversify across multiple sectors while maintaining value discipline. Moreover, different industries perform well during varying economic cycles.
Recommended sector allocation:
- 🏦 Financials: 25-30% of book value portfolio
- 🏭 Industrials: 20-25% allocation for cyclical exposure
- ⚡ Utilities: 15-20% for stability and dividends
- 🏠 Real estate: 10-15% through REITs and developers
- 🔧 Materials: 10-15% for commodity exposure
Position Sizing Guidelines Individual positions should balance concentration with diversification. However, high-conviction opportunities justify larger allocations. Moreover, smaller positions enable broader diversification across opportunities.
Position sizing framework:
- 📊 Core positions: 3-5% of portfolio for high-conviction picks
- 📊 Standard positions: 2-3% allocation for typical opportunities
- 📊 Speculative positions: 1-2% for higher-risk situations
- 📊 Maximum single position: Never exceed 8% regardless of conviction
Risk Management for Book Value Trading ⚠️
Book value investing involves specific risks requiring dedicated management strategies. Furthermore, accounting quality affects book value accuracy significantly. Therefore, understanding potential pitfalls becomes crucial for success.
Common Book Value Trading Risks
Asset Quality and Accounting Issues Book value depends on accurate asset valuations. However, accounting manipulation can inflate book values artificially. Moreover, obsolete assets may carry inflated balance sheet values.
Red flags for asset quality:
- 🚨 Goodwill representing large portion of book value
- 🚨 Inventory values increasing while sales decline
- 🚨 Long-term assets without recent impairment charges
- 🚨 Frequent accounting method changes or restatements
Value Trap Identification Some stocks trade below book value for legitimate reasons. Furthermore, declining industries may never recover to historical valuations. Additionally, management incompetence can destroy shareholder value permanently.
Value trap warning signs:
- 🚫 Consistently declining revenues over multiple years
- 🚫 Market share losses to disruptive competitors
- 🚫 Technology obsolescence affecting core business
- 🚫 Regulatory changes harming long-term prospects
Stop-Loss and Exit Strategies
Technical Stop-Loss Levels Combine fundamental analysis with technical stop-losses. Moreover, 15-20% maximum losses protect against major capital erosion. However, temporary volatility should not trigger stops prematurely.
Stop-loss implementation:
- 📉 Initial stop: 15% below entry price for individual stocks
- 📉 Trailing stop: Move up with significant price appreciation
- 📉 Fundamental stop: Exit if investment thesis breaks down
- 📉 Portfolio stop: Reduce exposure if multiple positions decline
Profit-Taking Guidelines Book value stocks often appreciate slowly requiring patience. However, significant overvaluation justifies profit-taking decisions. Furthermore, rebalancing maintains optimal portfolio allocation consistently.
Profit-taking triggers:
- 📈 P/B ratio exceeds 1.5-2.0 times depending on quality
- 📈 Stock price doubles from entry point
- 📈 Better opportunities emerge requiring capital reallocation
- 📈 Annual rebalancing to maintain target allocations
Advanced Book Value Analysis Techniques 💎
Sophisticated investors use enhanced book value methods. Moreover, adjustments for intangible assets improve accuracy significantly. Furthermore, understanding limitations prevents costly analytical mistakes.
Tangible Book Value Analysis
Removing Intangible Assets Tangible book value excludes goodwill and intangible assets. Therefore, it provides a more conservative valuation baseline. Additionally, tangible assets typically have clearer liquidation values.
Tangible book value calculation:
- 📊 Start with total shareholders’ equity
- 📊 Subtract goodwill from acquisitions
- 📊 Subtract other intangible assets (patents, trademarks)
- 📊 Divide result by shares outstanding
Price-to-Tangible Book Ratios P/TB ratios often exceed P/B ratios significantly. However, they provide more realistic asset-based valuations. Moreover, banks and financial companies commonly use this metric.
Economic Book Value Adjustments
Inflation-Adjusted Book Values Historical cost accounting understates current asset values. Therefore, replacement cost analysis provides better perspective. Furthermore, inflation affects long-held assets most significantly.
Replacement cost considerations:
- 🏭 Manufacturing equipment valued at historical costs
- 🏢 Real estate purchased decades ago at lower prices
- ⚡ Utility infrastructure with substantial replacement costs
- 📊 Natural resources developed at historical expenses
Hidden Asset Identification Some companies own valuable assets carried at minimal book values. Moreover, subsidiary investments may trade below holding company market values. Additionally, intellectual property often lacks balance sheet representation.
Common hidden assets:
- 🏠 Real estate held at historical cost basis
- 💎 Natural resource reserves with proven values
- 📺 Brand values not reflected in accounting
- 🏢 Subsidiary stakes trading below holding company valuation
Building Your Book Value Portfolio 🏗️
Systematic portfolio construction improves book value investing results. Furthermore, regular rebalancing maintains optimal allocations over time. Therefore, developing structured processes becomes essential for success.
Core-Satellite Approach
Core Holdings Strategy Core positions should represent 60-70% of book value portfolio. Moreover, these holdings emphasize stability and consistent returns. Additionally, core stocks typically pay dividends while appreciating.
Core position characteristics:
- 🎯 Large-cap companies with stable operations
- 🎯 Strong balance sheets with minimal debt
- 🎯 Consistent profitability over economic cycles
- 🎯 Dividend payments supported by cash flow
Satellite Opportunities Satellite positions enable higher returns through concentrated bets. However, they also involve elevated risks requiring smaller allocations. Furthermore, special situations often create satellite opportunities.
Satellite position examples:
- 🚀 Spin-off companies trading below fair value
- 🚀 Activist investor targets with catalyst potential
- 🚀 Cyclical companies at economic cycle bottoms
- 🚀 Small-cap value opportunities with growth potential
Rebalancing and Maintenance
Quarterly Portfolio Review Regular reviews ensure positions remain aligned with investment thesis. Moreover, quarterly analysis allows timely exits from deteriorating situations. Additionally, systematic reviews prevent emotional decision-making.
Quarterly review checklist:
- 📋 Verify book value growth for each position
- 📋 Check for fundamental business changes
- 📋 Assess relative valuations versus alternatives
- 📋 Rebalance positions exceeding target allocations
Annual Strategy Assessment Annual reviews enable broader strategy evaluation and adjustments. Furthermore, market conditions change requiring tactical modifications. However, avoid frequent strategy changes undermining long-term results.
Common Mistakes in Book Value Trading 🚨
Understanding typical errors helps investors avoid costly mistakes. Furthermore, book value investing requires patience that many lack. Therefore, recognizing behavioral biases becomes crucial for success.
Analytical Mistakes
Ignoring Asset Quality Not all book value is created equal. However, many investors focus solely on P/B ratios without examining underlying assets. Moreover, obsolete or impaired assets inflate book values artificially.
Asset quality evaluation:
- 🔍 Verify assets generate cash flow
- 🔍 Assess asset age and replacement needs
- 🔍 Compare book values to market values when possible
- 🔍 Understand industry-specific asset characteristics
Overlooking Debt Obligations High debt levels can eliminate book value advantages quickly. Furthermore, debt service requirements reduce available cash flows. Additionally, financial distress can force asset sales below book values.
Behavioral Mistakes
Impatience with Value Realization Book value investing requires extended time horizons. However, modern markets emphasize quarterly performance creating pressure. Moreover, value realization often takes 2-3 years minimum.
Patience development strategies:
- ⏰ Set realistic 3-5 year investment horizons
- ⏰ Focus on business fundamentals rather than stock prices
- ⏰ Reinvest dividends during waiting periods
- ⏰ Maintain conviction through temporary volatility
Chasing Past Performance Strong book value performance attracts momentum investors inappropriately. Furthermore, crowded trades often become value traps. Additionally, rotating into new opportunities maintains edge.
FAQs 🤔
What’s the difference between book value and market value? Book value represents accounting value based on balance sheet equity, while market value reflects current stock price. Market prices often diverge significantly from book values due to growth expectations, sentiment, and other factors.
Should I only buy stocks trading below book value? Not necessarily. Quality companies may justify premiums to book value through superior returns and growth prospects. Focus on reasonable valuations rather than arbitrary thresholds.
How often should I rebalance my book value portfolio? Quarterly rebalancing typically provides optimal results. However, major market dislocations may justify interim adjustments. Avoid excessive trading that increases costs unnecessarily.
What sectors work best for book value investing? Financials, utilities, industrials, and real estate traditionally work well. These sectors have substantial tangible assets and clearer valuations than technology or service companies.
How do I avoid value traps when buying cheap stocks? Focus on companies with stable or growing revenues, consistent profitability, and strong balance sheets. Avoid declining industries or companies with fundamental problems despite low valuations.
Can book value investing work in growth markets? Book value strategies often underperform during growth market phases. However, they typically outperform during market downturns and provide downside protection during volatile periods.
Conclusion
Book value trading provides a systematic approach to identifying undervalued investment opportunities. Moreover, this time-tested strategy emphasizes tangible assets over market sentiment. Furthermore, combining book value analysis with quality screening creates robust investment frameworks.
Success requires patience, discipline, and systematic execution rather than perfect timing. Additionally, understanding asset quality and industry dynamics improves selection accuracy significantly. Finally, regular portfolio maintenance and rebalancing ensure optimal long-term performance through varying market conditions.
Book value investing rewards investors who can think independently and maintain conviction during difficult periods while the market eventually recognizes fundamental value.

Hold a Master Degree in Electrical engineering from Texas A&M University.
African born – French Raised and US matured who speak 5 languages.
Active Stock Options Trader and Coach since 2014.
Most Swing Trade weekly Options and Specialize in 10-Baggers !
YouTube Channel: https://www.youtube.com/c/SuccessfulTradings
Other Website: https://237answersblog.com/